Interference
interference
interference, in physics, the net effect of the combination of two or more wave trains moving on intersecting or coincident paths. The effect is that of the addition of the amplitudes of the individual waves at each point affected by more than one wave.
constructive interference and destructive interference
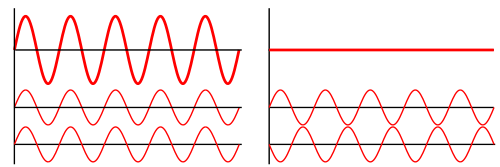
If two of the components are of the same frequency and phase (i.e., they vibrate at the same rate and are maximum at the same time), the wave amplitudes are reinforced, producing constructive interference; but, if the two waves are out of phase by 1/2 period (i.e., one is minimum when the other is maximum), the result is destructive interference, producing complete annulment if they are of equal amplitude
When two stones are dropped into a pool of water, waves spread out from each source, and interference occurs where they overlap. Constructive interference results where the crest of one coincides with the crest of the other. Two wave trains of light from a double slit produce interference, an effect that is visible on a screen as a pattern of alternating dark and light bands caused by intensification and extinction at points at which the waves are in phase and out of phase, respectively.
Phase
Interfence of different wavelengths or frequencies
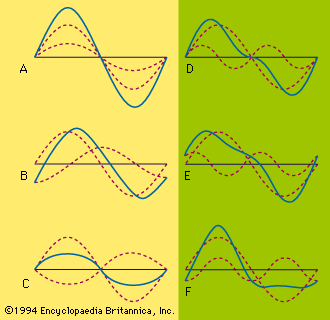 The solid line in Figures A, B, and C represents the resultant of two waves (dotted lines) of slightly different amplitude but of the same wavelength. The two component waves are in phase in Figure A but out of phase by 1/4 period and 1/2 period in B and C.
The solid line in Figures A, B, and C represents the resultant of two waves (dotted lines) of slightly different amplitude but of the same wavelength. The two component waves are in phase in Figure A but out of phase by 1/4 period and 1/2 period in B and C.
Interference also occurs between two wave trains moving in the same direction but having different wavelengths or frequencies. The resultant effect is a complex wave. A pulsating frequency, called a beat, results when the wavelengths are slightly different. Figures D, E, and F show complex waves (solid lines) composed of two component interfering waves (dotted lines), the ratio of their wavelengths being 1:2 and of their amplitudes 1:3
Newton's rings
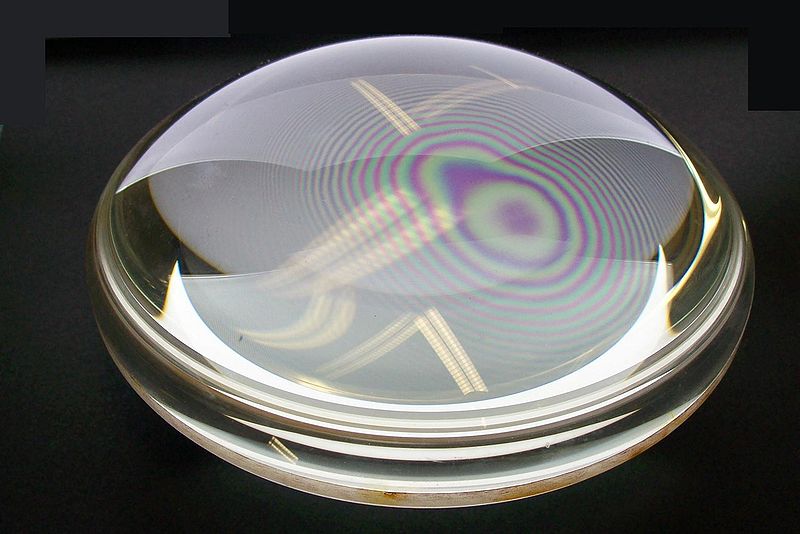
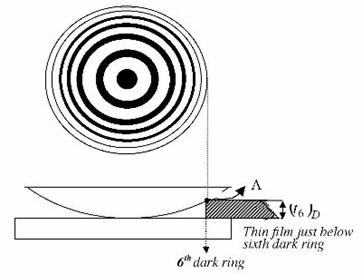 The phenomenon of Newton's rings, named after Isaac Newton who first studied them in 1717, is an interference pattern caused by the reflection of light between two surfaces - a spherical surface and an adjacent flat surface. When viewed with monochromatic light it appears as a series of concentric, alternating bright and dark rings centered at the point of contact between the two surfaces. When viewed with white light, it forms a concentric ring pattern of rainbow colors because the different wavelengths of light interfere at different thicknesses of the air layer between the surfaces. The light rings are caused by constructive interference between the light rays reflected from both surfaces, while the dark rings are caused by destructive interference.
The phenomenon of Newton's rings, named after Isaac Newton who first studied them in 1717, is an interference pattern caused by the reflection of light between two surfaces - a spherical surface and an adjacent flat surface. When viewed with monochromatic light it appears as a series of concentric, alternating bright and dark rings centered at the point of contact between the two surfaces. When viewed with white light, it forms a concentric ring pattern of rainbow colors because the different wavelengths of light interfere at different thicknesses of the air layer between the surfaces. The light rings are caused by constructive interference between the light rays reflected from both surfaces, while the dark rings are caused by destructive interference.
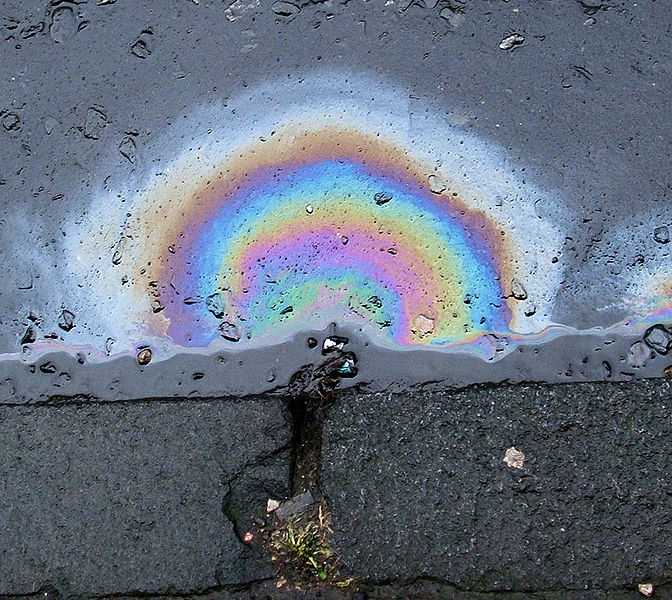
Thin film interferece
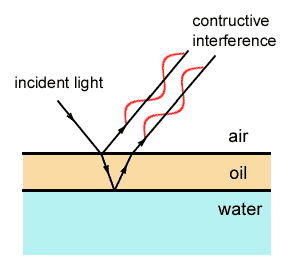
Thin-film interference is the phenomenon that occurs when incident light waves reflected by the upper and lower boundaries of a thin film interfere with one another to form a new wave. Studying this new wave can reveal information about the surfaces from which its components reflected, including the thickness of the film or the effective refractive index of the film medium. Thin films have many commercial applications including anti-reflection coatings, mirrors, and optical filters
